
Modernization of South Africa Payments – Foundations in Place
Read time: 7 min
The need for payments modernization
South Africa is a dynamic market — a leader and influencer in the African region. The South Africa Reserve Bank (SARB) has constantly aimed to modernize payment initiatives in consensus with banks and players in the market. As part of its payments modernization initiative, SARB published its Vision 2025 document in 2018, followed by a carefully planned industry-wide study on Asia to understand the various models and payments initiatives in 2019. The UPI model has been very successful and significantly revitalized the money movement throughout India. As a result, SARB started working closely with India and its related entities to receive guidance in setting up a real-time payments platform for South Africa.
The South African payments market has grown in recent years. The total transaction value is expected to show an annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 11.55 percent, resulting in a projected total of $23.86 billion by 2027. The below data establishes a high growth of digital transactions:
- From $8.88 billion in 2019, digital commerce transactions are expected to grow to $23.87 billion in 2027
- From $8.72 billion in 2019, digital remittances are expected to grow to $23.57 billion in 2027
- From $7.08 billion in 2019, mobile PoS payments are expected to grow to $17.94 billion in 2027
The South African market faced many challenges in enabling seamless money transfers. Limited options for immediate money transfers at different banks, lack of an instant settlement window for smaller amounts, and an inability to quickly request payments were critical factors that led to considering a real-time payments platform. The new platform started as an initiative in consultation with industry players and is set to be rolled out in two phases. The Vision 2025 document outlines the plans for SARB as highlighted below:
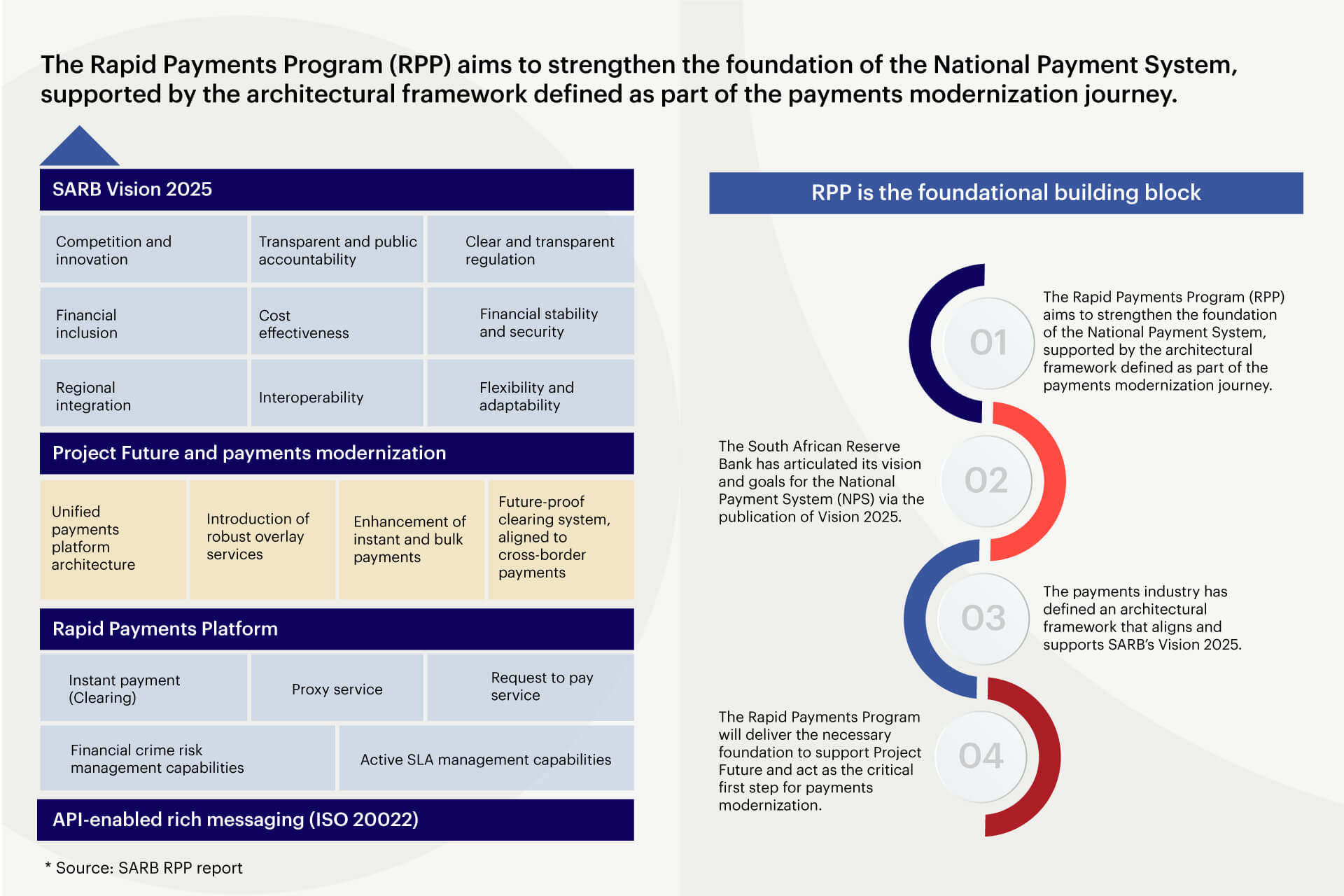
PayShap — a real-time payments platform (RPP)
The real-time payments platform, now called PayShap, offers the following capabilities:
- Pay by account: Payments between accounts.
- Pay by proxy: Payments without needing bank account details through proxy identifiers.
- Request to pay: Users can request payment from other users digitally.
- Instant settlements: Immediate posting of final and irrevocable funds and notifications.
The underlying enablers to create this ecosystem include an active SLA management system to ensure time-bound clearing and settlement and fraud checks to address transfer risk. This is built on an accessible national payments platform with industry-standard messaging structures in ISO 20022.
Ensuring interoperability is another key objective of this initiative. Interoperability between banks creates a healthy oligopolistic market with more dynamic access. This lays the foundation for rich interbank interactions and cooperation driven by the central bank, reducing fees over time.
PayShap intends to have a robust payments infrastructure that caters to multiple business segments and enables seamless money flow across the economy. With a focus on designing a viable alternative to cash payments and humanizing digital payments, PayShap is a platform infrastructure that ensures future modernization. It also aims to facilitate grant payments, thereby addressing the G2P market. This allows the country to roll out policy benefits and support for different sections of people directly through the payments infrastructure. Such a system has proven very effective, reducing pilferage and increasing government program efficiencies in countries where it has been implemented, such as India. Some of the advantages for different players in the market are highlighted below:
- Underbanked: The underbanked gain greater access to mainstream financial services
- Banked: Customers enjoy interoperability between payment rails
- Small merchants: Small merchants transact in hassle-free cashless methods
- Corporates: Corporates enjoy improved efficiencies in disbursements, payments, and business-related transactions
Target audience for digital payments
In South Africa, 53 percent of all point-of-sale purchases are made in cash. In the informal economy, approximately 89 percent of all transactions are cash-based.
PayShap provides viable digital options to customers. There are 64 million active mobile cellular subscribers in South Africa who will be the first target audience.
In addition to providing transfer services to the unbanked, PayShap facilitates the modernization of the money movement and payments market by providing suitable quick transfer options to merchants at the point of sale.
Roll out of PayShap
PayShap will be rolled out in two phases.
Phase 1: Pay by account and pay by proxy. Phase 1 will have four banks participating — ABSA, FNB, Standard Bank, and Ned Bank. The target date for this rollout is early 2023.
At launch, there will be a limit of 3000 Rands.
Phase 2: Request to pay (additional feature) will be introduced.
On the verge of something revolutionary
PayShap is a crucial initiative in the South African market for financial progress driven by broader participation, reach, and technological advancements. It will be necessary for the central governing authorities to create an inclusive ecosystem, facilitating continuous guidance and awareness to the financial institutions and customers on the process, security measures, and advantages of instant payment features. The launch of Payshap enables a platform for modernization and allows the government to bring in the infrastructure for the seamless transfer of grants and policy-based money distribution.
Ensuring interoperability and the instant settlement of funds, proxy payment, and request to pay would facilitate a systematic shift from cash-based to digitally-enabled transactions, providing better control and measurement options to the government and the central bank. It also facilitates identifying risk-based transfers and creates a strong growth and innovation platform. The existing high fee structures for payments have been a point of contention for years. PayShap transaction charges will play a key role in its adoption. If priced effectively, this can drive rapid market transformation and financial inclusion. For this, SARB needs to closely monitor the phase 1 rollout, provide constant support to the participants, and constantly update process and technology changes as required.
In addition, Payshap has the potential to revolutionize the digital payments space, leading to the proliferation of FinTechs and dynamism in the financial services ecosystem. This creates healthy competition between players, ensuring better quality and more economical services to end customers.









