
Product Discovery: Key to a Successful Market Launch
What is product discovery?
Product discovery is a research and experimentation process that helps organizations understand their customers and design better products for them. It is the first step in the software development cycle and sets the foundation for the project. It involves activities that help identify, validate, and prioritize product ideas and features.
The purpose of product discovery is to uncover the following:
- Is the product compelling enough for the customer to use?
- Does it solve the most challenging problems?
- Can businesses capture its value and monetize the product usage?
- Can customers figure out how to use the product?
- Do capabilities exist within the organization to build the products?
Addressing these concerns helps create a product that meets customer needs and can be built within the given time and budget constraints. Additionally, this helps organizations reduce uncertainty and risk of failure, accelerate time-to-market, and increase customer satisfaction.
Why is product discovery so important?
Product discovery helps organizations understand what products or services their customers need or want. This can lead to the development of new products or the improvement of existing ones, which can, in turn, help organizations grow and stay competitive in the market. Product discovery involves:
- Uncovering new opportunities: Identifying unmet customer needs and developing solutions to address them, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced risk of failure: Product teams gather feedback from potential customers to validate assumptions and refine the product idea, so risks are tackled upfront, not in the delivery phase.
- Prioritization: Product discovery helps product teams prioritize high-impact features that can increase the product adoption rate and maximize return on investment.
- Validated learning: Products are defined and designed collaboratively rather than sequentially, which creates faster learning opportunities and reduced time-to-market.
- Stakeholder alignment: Product discovery helps build consensus and alignment with multiple stakeholders, resulting in a substantiated product backlog.
Who should conduct product discovery?
The Product team is the heart of any successful product. It’s their job to bring the product to life and ensure it meets customer needs. In today’s world, technology drives design, and design drives and enables business functionality. Functionality, design, and technology are intrinsically entwined. As such, the team must be carefully selected to ensure the right mix of skills, personalities, and experience.
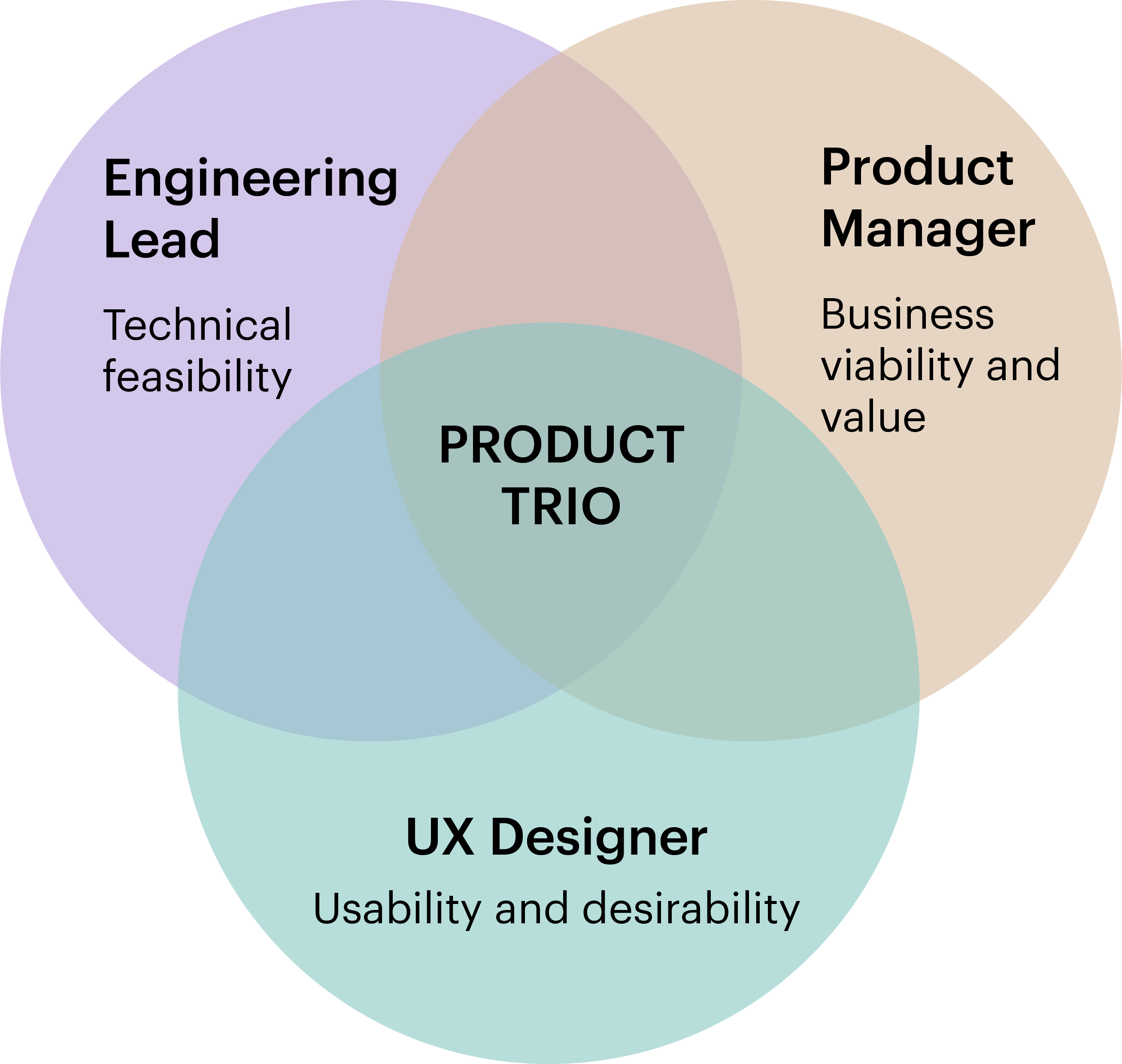
Fig 1: The Product Trio
A popular framework for onboarding the right Product team is the Product Trio. The Product Trio is a cross-functional team comprises of a Product Manager, an Engineering Lead, and a UX Research/Designer. Members of this team are permanent collaborators on the product through the phases of product discovery and delivery. So, each member of the Product Trio needs to come together early in the discovery phase to clearly understand how the product will solve customer problems.
The Product Manager is responsible for defining the viability of the product, the product roadmap, and ensuring that the product meets customer needs. The Engineering Lead is responsible for identifying the technical feasibility, and the UX Designer is responsible for the user experience and the overall look and feel.
Each member of the Product Trio brings a unique set of skills and experience to the table. When the right people take up these three roles, the team is set up for success.
When should product discovery be conducted?
The product discovery process is typically triggered by identifying a problem or opportunity. This could be a problem that customers are facing or a new market trend that presents a potential opportunity for the business.
The initial product discovery runs without product delivery. Its goal is to discover a product that has a customer base and a chance of achieving the right market fit. This can typically be true for start-ups and mature organizations trying to build something new outside their core businesses. The initial product discovery phase can run on multiple iterations called discovery/design sprints, where teams can try out and evaluate each new idea for maximum customer and business impact.
Continuous product discovery is adopted in products that have achieved a market fit and are being used by an existing set of customers. These are usually products in the growth stage of the product life cycle, where new features or requests need to be built to make the product more appealing. Continuous discovery is an exercise that overlaps and intertwines with delivery, helping Product teams become more efficient and deliver high impact. When the discovery is an ongoing process, it becomes easier to uncover innovative ideas, evaluate customer value, and bring stakeholder alignment with the product vision.
In large organizations, continuous discovery will also focus on avoiding risky product discovery activities, protecting the brand image, and building consensus among multiple stakeholders.
How is product discovery conducted?
In product discovery, teams typically work on two key areas:
- Problem space: Digging into details to get a deeper understanding of the challenges and pains of users, customers, and stakeholders. Customer interviews, data analysis, product usage/adoption patterns, and market research trends are handy techniques that enable this.
- Solution space: Mapping solutions that address the pain points through creative ideas, building prototypes, testing, and capturing feedback from target users. Here, techniques of brainstorming, formulating a hypothesis, and experimentation to validate assumptions are helpful.
As a best practice, the Product teams must emphasize understanding the users and problem space, as this effectively solves the right problem for the right set of target users. Ash Maurya, the Founder of LEANSTACK, rightly quotes, “Love the problem, not your solution.”
The most popular method used in product discovery is the Double Diamond approach to discover customer problems and explore creative solutions. Its four elements are:
- Discover – exploring the problem space.
- Define – interpreting the findings and defining the problem statement.
- Ideate – identifying viable solutions.
- Validate – prototyping, collecting feedback, and validating solutions.
The illustration below describes the steps in the Double Diamond framework, the activities performed, and the techniques and tools used in each stage of the discovery process.
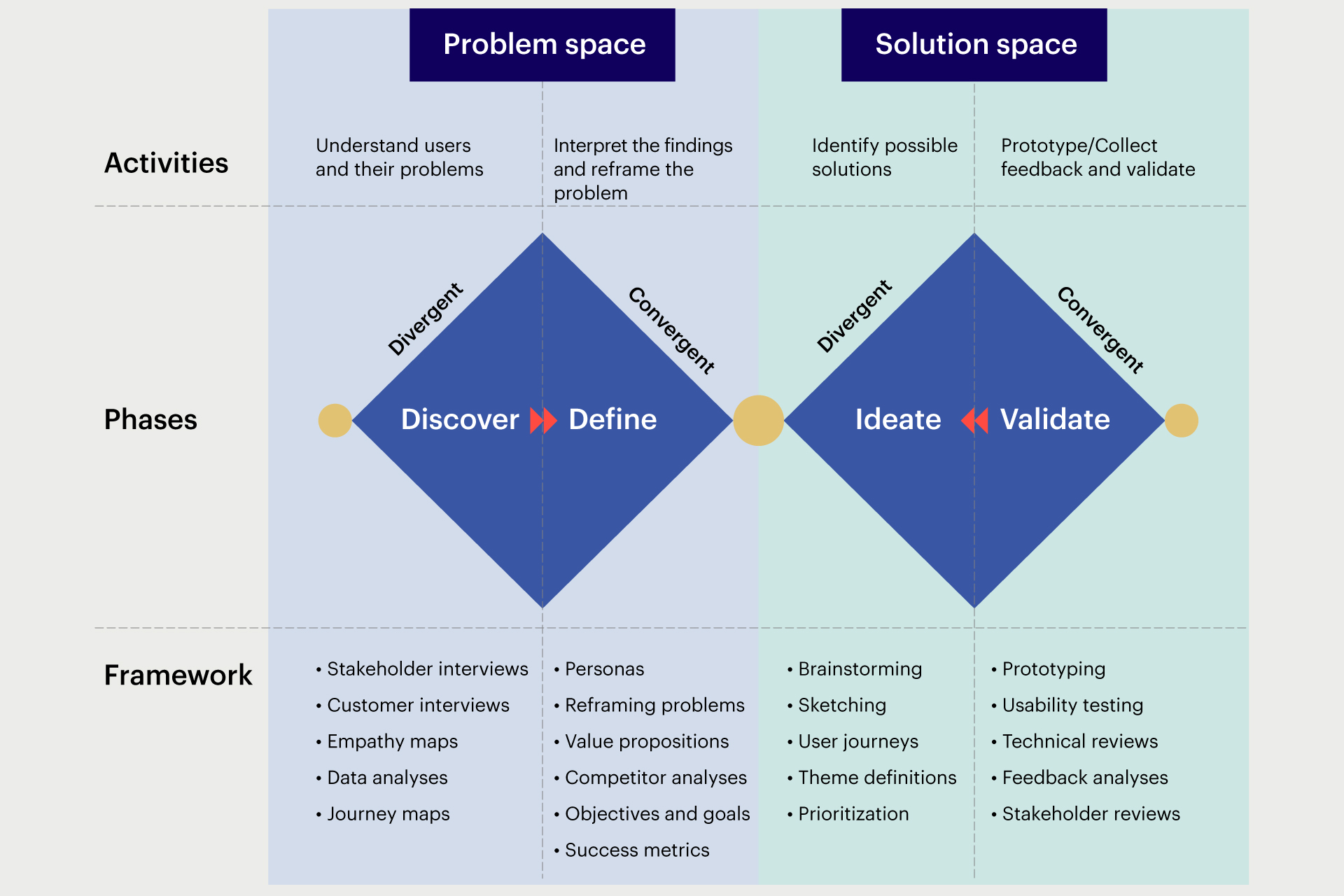
Fig 2: Double Diamond Framework
Product discovery and product delivery
Product discovery and product delivery are two distinct stages in product development. Product discovery describes activities performed to decide on building the right product. The primary objective is to validate ideas in the fastest and cheapest way possible.
Product delivery is the work done to build the product right, the actual development of the product. Without running discovery, building a product can turn out to be a slow and expensive way to validate an idea.
Dual-track Agile, as advocated by Marty Cagan, is an approach to product development that combines discovery and delivery methods. It involves two parallel tracks: the discovery track focuses on exploring and defining the problem or opportunity using design thinking methods, while the delivery track focuses on delivering the solution to that problem through agile development.
In combining these two approaches, Dual-track Agile allows Product teams to quickly explore and validate potential solutions while allowing the delivery track to focus on delivering working software for validated solutions in a timely manner. This helps teams develop high-quality products that are effective and efficient.
In Dual-track Agile, the workflow is not characterized by each role delivering artifacts onto the next step; it is collaborative – the Product Manager, Designer, and Lead Engineer work side-by-side to create and validate backlog items.
Getting it right
To conclude, product discovery can help companies develop products that better meet the needs of their customers, improve the efficiency and effectiveness of product development, and reduce the risk of developing products that fail to deliver value.
References
- SVPG article on discovery and delivery
- Product talk on principles of product discovery
- Dual Track Agile by Marty Cagan